W-2 vs 1099 Explained: Contractor vs Employee Rules, Deadlines, Errors & Corrections
Hiring workers is a major milestone for any business—but it also comes with serious tax and compliance responsibilities. One of the most common and costly mistakes U.S. employers make is misclassifying workers and mishandling W-2 and 1099 filings.
This guide explains everything employers need to know about W-2 vs 1099, IRS worker classification rules, filing deadlines, common mistakes, and how to fix errors correctly—before they turn into penalties or audits.
Whether you run a startup, small business, or growing company, this article will help you stay compliant and confident.
📑 Table of Contents
What Are W-2 and 1099 Forms?
W-2 vs 1099: Key Differences Employers Must Know
Contractor vs Employee: IRS Classification Rules
Common W-2 & 1099 Filing Errors (And How to Avoid Them)
W-2 and 1099 Filing Deadlines Explained
How to Correct W-2 or 1099 Filing Mistakes
Why Professional Filing Matters
Final Thoughts
1️⃣ What Are W-2 and 1099 Forms?
Before diving into rules and deadlines, it’s important to understand what these forms are and why they matter.
What Is a W-2?
A W-2 form reports wages paid to employees and shows taxes withheld, including:
Federal income tax
Social Security tax
Medicare tax
State and local taxes (if applicable)
Employers are responsible for withholding and paying payroll taxes for W-2 employees.
What Is a 1099?
A 1099-NEC or 1099-MISC reports payments made to independent contractors or non-employees.
No payroll taxes are withheld by the employer.
Contractors are responsible for paying their own:
Income taxes
Self-employment taxes
2️⃣ W-2 vs 1099: Key Differences Employers Must Know
| Category | W-2 Employee | 1099 Contractor |
|---|---|---|
| Employment status | Employee | Independent contractor |
| Tax withholding | Yes | No |
| Employer payroll taxes | Required | Not required |
| Benefits | Often provided | Not provided |
| Work control | Employer controls | Contractor controls |
| Tax form issued | W-2 | 1099-NEC / 1099-MISC |
👉 Bottom line: The form you issue depends on the true working relationship, not what you “call” the worker.
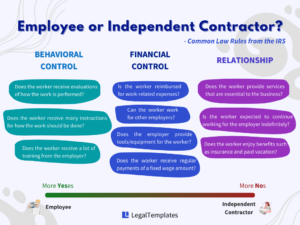
3️⃣ Contractor vs Employee: IRS Classification Rules Explained
The IRS uses three main factors to determine worker classification.
1. Behavioral Control
Does the business control how, when, and where the work is done?
Are training and instructions provided?
👉 More control = Employee
2. Financial Control
Does the worker invest in their own tools?
Can they work for multiple clients?
Are they paid per project instead of hourly?
👉 More independence = Contractor
3. Relationship Type
Are there benefits like insurance or paid leave?
Is the relationship ongoing or project-based?
Is the work a key part of the business?
👉 Long-term + benefits = Employee
⚠️ Misclassification risk: Incorrectly classifying an employee as a contractor can trigger back taxes, penalties, and audits.
4️⃣ Common W-2 & 1099 Filing Errors (And How to Avoid Them)
Many penalties happen due to simple but avoidable mistakes.
❌ Most Common Errors
Issuing 1099s to workers who should be W-2 employees
Missing or incorrect Social Security numbers
Filing after deadlines
Using the wrong form (1099-MISC instead of 1099-NEC)
Not filing state copies
Mathematical errors or mismatched totals
Forgetting electronic filing requirements
✅ How to Avoid These Errors
Classify workers correctly from day one
Collect W-9 forms from contractors early
Reconcile payroll and contractor payments monthly
Use professional payroll/accounting support
File early—not at the last minute
5️⃣ W-2 and 1099 Filing Deadlines Explained
Missing deadlines is one of the fastest ways to get penalized.
📅 W-2 Deadlines
Employee copies: January 31
SSA filing: January 31
📅 1099 Deadlines
1099-NEC (contractors): January 31
1099-MISC:
Recipient: January 31
IRS (paper): February 28
IRS (electronic): March 31
⚠️ Deadlines apply every year, even if no taxes were withheld.
6️⃣ How to Correct W-2 or 1099 Filing Mistakes
Mistakes happen—but ignoring them makes things worse.
Correcting W-2 Errors
Use Form W-2c (Corrected Wage and Tax Statement)
File corrected copies with:
Employee
Social Security Administration
Pay any underpaid taxes immediately to reduce penalties
Correcting 1099 Errors
File a Corrected 1099 with the IRS
Send corrected copy to the contractor
Clearly mark it as “Corrected”
Re-file state copies if required
👉 The faster you correct mistakes, the lower the penalties.
7️⃣ Why Professional Filing Matters
W-2 and 1099 compliance isn’t just paperwork—it’s risk management.
Professional accounting support helps you:
Classify workers correctly
Meet all federal and state deadlines
Avoid IRS penalties and audits
Handle multi-state filings smoothly
Fix mistakes properly and quickly
For businesses operating across multiple states or hiring remote workers, professional oversight is no longer optional—it’s essential.
8️⃣ Final Thoughts
Understanding W-2 vs 1099, worker classification rules, filing deadlines, and correction procedures protects your business from unnecessary risk.
The cost of doing it wrong is far higher than the cost of doing it right the first time.
If you’re unsure about your worker classifications, filings, or past mistakes, now is the time to act—before the IRS acts first.
📞 Get Started Today
Live Calls: +1-281-819-8806
Support: 713-322-0834
Email: Support@usaaccounting.online
WhatsApp: +1-832-832-0751
👉 Schedule Your Free Consultation
W-2 vs 1099 Explained: Contractor vs Employee Rules, Deadlines, Errors & Corrections
W-2 vs 1099 Explained: Contractor vs Employee Rules, Deadlines, Errors...
Read MorePersonal vs Business Taxes: A Stress-Free Guide to Preparing for Tax Season
Personal vs Business Taxes: A Stress-Free Guide to Preparing for...
Read MoreMonthly vs Quarterly Bookkeeping: What’s Best for Your Business?
📊 Monthly vs Quarterly Bookkeeping: What’s Best for Your Business?...
Read MoreWeekly vs Bi-Weekly vs Monthly Payroll: Which One Should You Choose?
Weekly vs Bi-Weekly vs Monthly Payroll: Which One Should You...
Read More